Morbus Parkinson Substantia Nigra

Cell loss in the parkinsonian snpc can be appreciated macroscopically.
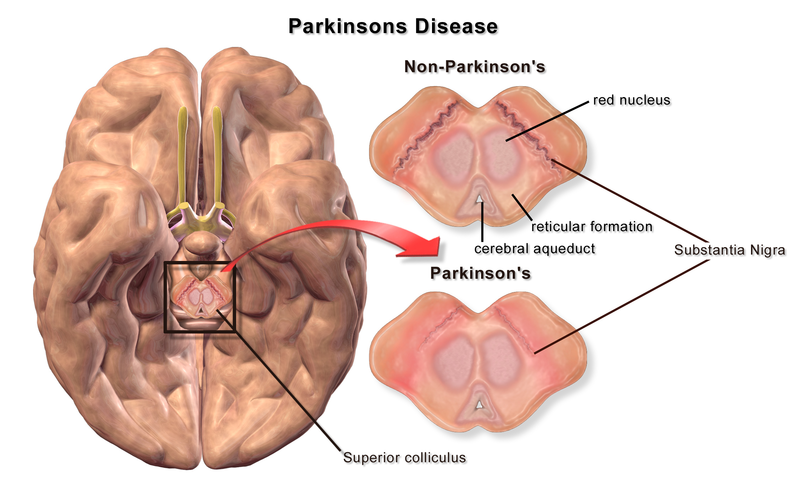
Morbus parkinson substantia nigra. Parkinson is the deterioration of dopaminergic neurons in the mid brain specifically in the substantia nigra sn black substance. Parkinson disease pd also known as idiopathic parkinsonism is a neurodegenerative disease and movement disorder characterized by resting tremor rigidity and hypokinesia due to progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra. Parkinson s disease is a devastating condition whereby neurons in a specific region of the brain that controls movement lose functionality or die. This brain region is known as the substantia nigra which is latin for black substance due to the fact that it contains a high concentration of neuromelanin containing dopaminergic neurons.
The substantia nigra pars compacta snpc can be identified by tyrosine hydroxylase th immunostaining reflecting the presence of dopaminergic da neurons. A characteristic sign of m. Different causes and forms of this disease have been identified. This structure produces also the transmitter substance dopamine.
It is a risk marker for pd and associated with altered microstructural changes in white matter including those areas relevant for motor and limbic function. Parkinson s disease is a chronic degenerative organic disease with unknown causes. Parkinson s disease is characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Nerve cells in the substantia nigra send out fibers to tissue located in both sides of the brain.
The brain stem in particular the midbrain structure the substantia nigra black substance is significantly affected by a high rate of cellular death of dopamine secreting cells. Substantia nigra sn hyperechogenicity was determined by transcranial sonography tcs in pd patients. Part of the disease process develops as cells are destroyed in certain parts of the brain stem particularly the crescent shaped cell mass known as the substantia nigra. The loss of specific populations of cells in the brain such as the dopamine producing neurons in a region called the substantia nigra which lies in an area called the midbrain at the base of the brain top of the brain stem.
Parkinson disease is a slowly progressive disorder that affects movement muscle control and balance. A disappearance of cells with melanin in the substantia nigra is considered as biological artefact of the disease which causes a degenerative loss of neurons in the corpus striatum of mesencephalon. The substantia nigra is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement.